| title | date | categories | tags | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
RISC-V Trap |
2024-04-22 17:30:00 +0800 |
|
|
在 ISA 语境下,trap 包括异常和中断。
在 OS 语境下,trap 包括异常、系统调用(其实也是一种异常)、中断。
-
Exception
We use the term exception to refer to an unusual condition occurring at run time associated with an instruction in the current RISC-V hart.
-
Interrupt
We use the term interrupt to refer to an external asynchronous event that may cause a RISC-V hart to experience an unexpected transfer of control.
-
Trap
We use the term trap to refer to the transfer of control to a trap handler caused by either an exception or an interrupt.
-
Trap 处理总流程
- 什么条件下 trap 进什么 mode
- 进入 trap 时的 CPU 操作
- 进入 trap 以后的软件操作
- 退出 trap 时的 CPU 操作
-
进入和退出 trap 时的 CPU 操作
-
mstatus的一部分就是sstatusA restricted view of
mstatusappears as thesstatusregister in the S-level ISA.The
sstatusregister is a subset of themstatusregister. -
读写
sstatus等于读写mstatusIn a straightforward implementation, reading or writing any field in
sstatusis equivalent to reading or writing the homonymous field inmstatus. -
发生 trap
When a trap is taken from privilege mode y into privilege mode x, xPIE is set to the value of xIE; xIE is set to 0; and xPP is set to y.
从 y 进入 x,xPIE = xIE、xIE = 0、xPP = y。
另外,xepc = pc、xcause xtavl 更新、pc = xtvec。
-
从 trap 返回
When executing an xRET instruction, supposing xPP holds the value y, xIE is set to xPIE; the privilege mode is changed to y; xPIE is set to 1; and xPP is set to the least-privileged supported mode (U if U-mode is implemented, else M).
执行 xRET,xIE = xPIE,特权级 = xPP、xPIE = 1、xPP = U。
另外,xRET 使 pc = xepc。
MRET:MIE = MPIE,特权级 = MPP、MPIE = 1、MPP = U、pc = mepc。
SRET:SIE = SPIE,特权级 = SPP、SPIE = 1、SPP = U、pc = sepc。
-
-
什么条件下 trap 进什么 mode
下面讨论。
如果同时出现 exception 和 interrupt,先处理谁 RISC-V 文档没有规定。老版本是有的,后来不知道为什么删了。
-
首先,如果不使用代理,所有 trap 都会进入 m mode 处理
By default, all traps at any privilege level are handled in machine mode, though a machine-mode handler can redirect traps back to the appropriate level with the MRET instruction (Section 3.3.2).
-
代理就是进入 s mode 处理,但是不可能进入 u mode
To increase performance, implementations can provide individual read/write bits within
medelegandmidelegto indicate that certain exceptions and interrupts should be processed directly by a lower privilege level.In systems with S-mode, the
medelegandmidelegregisters must exist, and setting a bit inmedelegormidelegwill delegate the corresponding trap, when occurring in S-mode or U-mode, to the S-mode trap handler. -
代理的用处
- 在 S 态发生异常或中断时,可以直接在 S 态处理
- 在 U 态发生异常或中断时,不用升到 M 态,升到 S 态就可以
-
Contents of registers
For exceptions that cannot occur in less privileged modes, the corresponding
medelegbits should be read-only zero. In particular,medeleg[11] (ecall from m-mode) is read-only zero.mideleg实际上只有 3 位可以读写,对应 SEI STI SSI。 -
处理 trap 时特权级不会降低,只会不变或者升高
Traps never transition from a more-privileged mode to a less-privileged mode.
For example, if M-mode has delegated illegal instruction exceptions to S-mode, and M-mode software later executes an illegal instruction, the trap is taken in M-mode, rather than being delegated to S-mode.
By contrast, traps may be taken horizontally. Using the same example, if M-mode has delegated illegal instruction exceptions to S-mode, and S-mode software later executes an illegal instruction, the trap is taken in S-mode.
-
什么条件下 trap 进什么 mode(异常)
对某一个异常,如果它没被代理,不管处理器现在是 u/s/m,发生异常以后,都会进入 m-mode。
对某一个异常,如果它被代理了,就意味着发生异常以后会进入 s-mode。
如果处理器现在是 m,发生异常以后,代理无效,进入 m-mode。
如果处理器现在是 s,发生异常以后,代理有效,进入 s-mode。
如果处理器现在是 u,发生异常以后,代理有效,进入 s-mode。
如果发生多个异常,根据异常优先级进行处理。
-
什么条件下 trap 进什么 mode(中断)
什么条件下 trap 进什么 mode(中断)实际上分成两部分,包括中断硬件和 CPU。
可以被代理的中断实际上只有 SEI STI SSI,下面讨论。
-
External interrupt
-
Timer interrupt
-
Software interrupt
Software interrupts are most useful for interprocessor communication in multi-hart systems, as harts may write each other’s
MSIPbits to effect interprocessor interrupts. (SiFive Doc)
市面上的 SOC 大多只实现了 PLIC 和 CLINT。
-
Platform-Level Interrupt Controller (PLIC)
https://github.com/riscv/riscv-plic-spec
最早由 SiFive 提出并实现,现在已经被标准化。
产生 s-mode m-mode external interrupt。
-
Core-Local Interruptor (CLINT)
https://www.sifive.com/documentation
最早由 SiFive 提出并实现,CLINT 文档包含在 SiFive SOC 文档中。RISC-V 官方没有文档。
产生 m-mode timer interrupt 和 m-mode software interrpt。
这些高级中断硬件还没有硬件实现。
-
Core-Local Interrupt Controller (CLIC)
https://github.com/riscv/riscv-fast-interrupt
只负责 local interrupt。
-
Advanced Interrupt Architecture (AIA)
https://github.com/riscv/riscv-aia
MSI 好像是 PCIE 引入的概念。
– Extended Local Interrupts (AIA CSRs) – Incoming Message Signaled Interrupt Controller (IMSIC) – Advanced Platform Level Interrupt Controller (APLIC)
-
Advanced Core-Local Interruptor (ACLINT)
https://github.com/riscv/riscv-aclint
ACLINT 兼容 CLINT。
-
中断仲裁(什么条件下 trap 进什么 mode)
满足下面条件的中断源会参与中断仲裁:
- 中断源的 IP 为 1(中断源发生电平中断或脉冲中断会将 IP 置 1)
- 中断源的优先级 PRIO 大于 0
- 中断源的 MIE/SIE 寄存器打开
仲裁时先看优先级,高的优先;如果优先级一样,中断号小的优先。
仲裁结果是中断号。
-
Interrupt notification(什么条件下 trap 进什么 mode)
Interrupt notifications generated by the PLIC appear in the meip/seip bits of the mip/sip registers for M/S modes respectively.
当仲裁结果的优先级大于 MTH/STH 寄存器时,会向中断目标发送中断提醒,即将 mip sip 中的 MEIP SEIP 置 1。
如果 PLIC 向同一个 hart 的不同特权级都发送中断提醒,那么 mip 的 MEIP SEIP 都会置 1。如果 SEIP 被代理,sip 中的 SEIP 也会置 1;如果 SEIP 不被代理,sip 中的 SEIP 是 0。
-
中断 claim(进入 trap 以后的软件操作)
中断目标读 MCLAIM/SCLAIM 寄存器,读出仲裁结果的中断号。然后 PLIC 将该中断源的 IP 置 0,且在中断处理完成之前屏蔽该中断源的后续采样。
在 claim 以后,如果存在其他中断,xEIP 位可能还会是 1。
xEIP 位为 0 时也可以 claim。
-
中断 completion(进入 trap 以后的软件操作)
中断目标将中断号写入 MCLAIM/SCLAIM 寄存器。(该写操作不会更新 CLAIM 寄存器。)然后 PLIC 解除中断号对应的中断源采样屏蔽,结束整个中断处理过程。
The PLIC does not check whether the completion ID is the same as the last claim ID for that target.
RISC-V 文档只提到了 mtime 和 mtimecmp,关于 msip,只在说明 mip.MSIP 时说可以通过写 mmio 寄存器来更新 mip.MSIP,具体没说这个 mmio 寄存器是什么。
-
msipregister (memory-mapped, 1 for each hart)Machine-mode software interrupts are generated by writing to the memory-mapped control register
msip. (SiFive Doc)The least significant bit of
msipregister is reflected in theMSIPbit of themipCSR. (SiFive Doc) -
mtimecmpregister (memory-mapped, 1 for each hart)A machine timer interrupt becomes pending whenever
mtimecontains a value greater than or equal tomtimecmp, treating the values as unsigned integers.The timer interrupt is reflected in the
MTIPbit of themipregister. (SiFive Doc)Writes to
mtimeandmtimecmpare guaranteed to be reflected inMTIPeventually, but not necessarily immediately. -
mtimeregister (memory-mapped, 1 for each platform)
-
单个中断进入 m-mode 的条件
An interrupt i will trap to M-mode (causing the privilege mode to change to M-mode) if all of the following are true:
- either the current privilege mode is M and the
MIEbit in themstatusregister is set, or the current privilege mode has less privilege than M-mode; - bit i is set in both
mipandmie; - if register
midelegexists, bit i is not set inmideleg.
- either the current privilege mode is M and the
-
单个中断进入 s-mode 的条件
An interrupt i will trap to S-mode if both of the following are true:
- either the current privilege mode is S and the
SIEbit in thesstatusregister is set, or the current privilege mode has less privilege than S-mode; and - bit i is set in both
sipandsie.
- either the current privilege mode is S and the
-
当有中断可以 trap 进 m,也有中断可以 trap 进 s
Interrupts to M-mode take priority over any interrupts to lower privilege modes.
Interrupts to S-mode take priority over any interrupts to lower privilege modes.
-
多个 trap 进 m 的中断仲裁
Multiple simultaneous interrupts destined for M-mode are handled in the following decreasing priority order: MEI, MSI, MTI, SEI, SSI, STI.
-
多个 trap 进 s 的中断仲裁
Multiple simultaneous interrupts destined for supervisor mode are handled in the following decreasing priority order: SEI, SSI, STI.
-
什么条件下 trap 进什么 mode
外部中断硬件在这一步中起的作用是将 mip sip 中的位进行设置。
然后 CPU 首先根据 mip sip 中的位判断对应的单个中断什么条件下 trap 进什么 mode。如果存在 trap 进 m 的中断,也存在 trap 进 s 的中断,m 优先级高。然后再进行同一模式中断的仲裁,仲裁出一个中断。
-
How to set/clear
mipbitEach individual bit in register
mipmay be writable or may be read-only.When bit i in
mipis writable, a pending interrupt i can be cleared by writing 0 to this bit.If interrupt i can become pending but bit i in
mipis read-only, the implementation must provide some other mechanism for clearing the pending interrupt. -
mipbitMEIPread-onlyMEIPis read-only inmip, and is set and cleared by a platform-specific interrupt controller. -
mipbitMTIPread-onlyMTIPis read-only inmip, and is cleared by writing to the memory-mapped machine-mode timer compare register. -
mipbitMSIPread-onlyMSIPis read-only inmip, and is written by accesses to memory-mapped control registers. -
mipbitSEIPwritableSEIPis writable inmip, and may be written by M-mode software to indicate to S-mode that an external interrupt is pending.Additionally, the platform-level interrupt controller may generate supervisor-level external interrupts.
Supervisor-level external interrupts are made pending based on the logical-OR of the software-writable
SEIPbit and the signal from the external interrupt controller.When
mipis read with a CSR instruction, the value of theSEIPbit returned in the rd destination register is the logical-OR of the software-writable bit and the interrupt signal from the interrupt controller, but the signal from the interrupt controller is not used to calculate the value written toSEIP.Only the software-writable
SEIPbit participates in the read-modify-write sequence of a CSRRS or CSRRC instruction. -
mipbitSTIPwritableSTIPis writable inmip, and may be written by M-mode software to deliver timer interrupts to S-mode. -
mipbitSSIPwritableSSIPis writable inmipand may also be set to 1 by a platform-specific interrupt controller.
-
SEI STI SSI 只有被代理了能在
sipsie中有效Restricted views of the
mipandmieregisters appear as thesipandsieregisters for supervisor level.If an interrupt is delegated to S-mode by setting a bit in the
midelegregister, it becomes visible in thesipregister and is maskable using thesieregister.Otherwise, the corresponding bits in
sipandsieare read-only zero. -
读写 sip sie 中的位就是读写 mip mie 中的位
The
sipandsieregisters are subsets of themipandmieregisters. Reading any implemented field, or writing any writable field, ofsip/sieeffects a read or write of the homonymous field ofmip/mie. -
How to set/clear
sipbitEach individual bit in register
sipmay be writable or may be read-only.When bit i in
sipis writable, a pending interrupt i can be cleared by writing 0 to this bit.If interrupt i can become pending but bit i in
sipis read-only, the implementation must provide some other mechanism for clearing the pending interrupt (which may involve a call to the execution environment). -
sipbitSEIPread-onlyIf implemented,
SEIPis read-only insip, and is set and cleared by the execution environment, typically through a platform-specific interrupt controller. -
sipbitSTIPread-onlyIf implemented,
STIPis read-only insip, and is set and cleared by the execution environment. -
sipbitSSIPwritableIf implemented,
SSIPis writable insipand may also be set to 1 by a platform-specific interrupt controller.
-
几个重要信息
- 中断进入 m mode 的条件
- 中断进入 s mode 的条件
- SEI STI SSI 只有被代理了能在
sipsie中有效
-
中断处理汇总
-
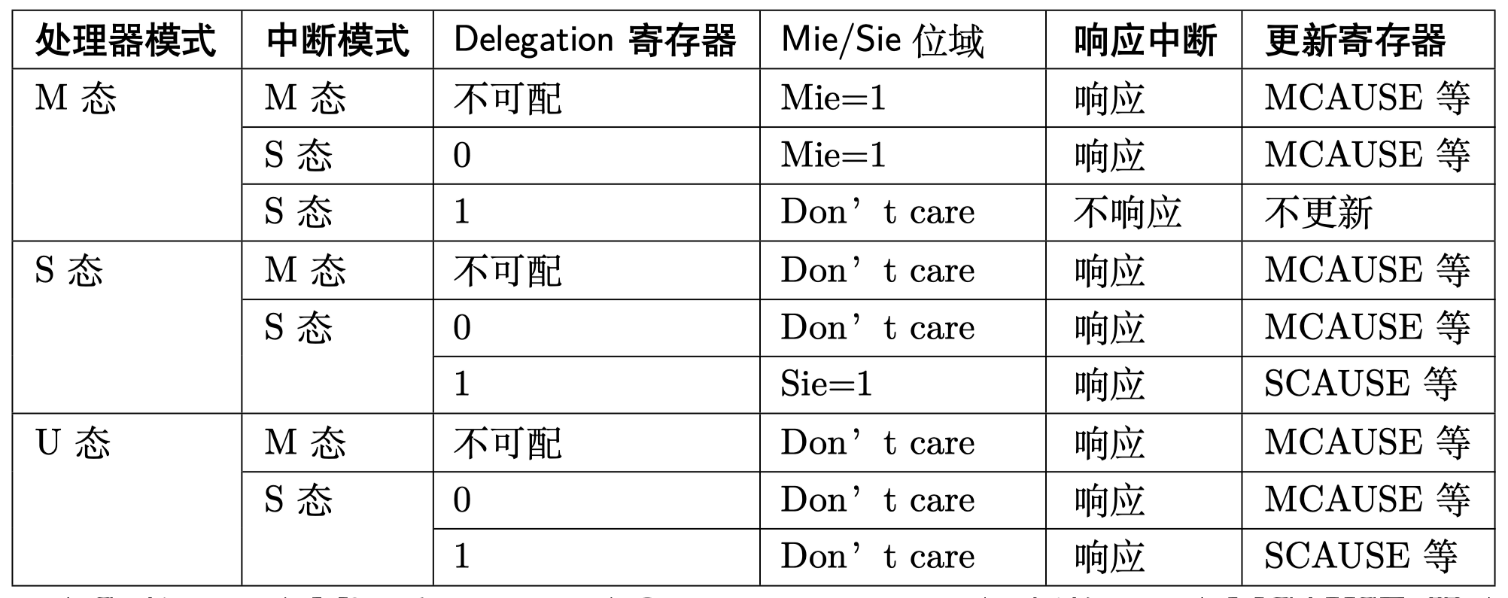
处理器 u,中断 m
m 态中断不能被代理。
根据信息 1,如果满足下列条件,trap 进 m-mode:
- 此时处理器为 u,不关心 mstatus 的 MIE
- mip mie 相应的位需要为 1,MEIP MTIP MSIP 都是 read-only,由 PLIC CLINT set clear
- m 态中断不能被代理
-
处理器 u,中断 s
s 态中断可以被代理。
如果没被代理,根据信息 1,如果满足下列条件,trap 进 m-mode:
- 此时处理器为 u,不关心 mstatus 的 MIE
- mip mie 相应的位需要为 1,SEIP STIP SSIP 都是 writable,SEIP 也可以由 PLIC set clear
- s 态中断没有被代理
如果被代理,根据信息 1 第 3 条,不能进 m-mode。根据信息 2,如果满足下列条件,trap 进 s-mode:
- 此时处理器为 u,不关心 sstatus 的 SIE
- 根据信息 3,此时中断已经被代理,sip sie 中可以看到 mip mie 的 SEI STI SSI,只要相应的位为 1 就可以
-
处理器 s,中断 m
根据信息 1,如果满足下列条件,trap 进 m-mode:
- 此时处理器为 s,不关心 mstatus 的 MIE
- mip mie 相应的位需要为 1,MEIP MTIP MSIP 都是 read-only,由 PLIC CLINT set clear
- m 态中断不能被代理
-
处理器 s,中断 s
如果中断没被代理,根据信息 1,如果满足下列条件,trap 进 m-mode:
- 此时处理器为 s,不关心 mstatus 的 MIE
- mip mie 相应的位需要为 1,SEIP STIP SSIP 都是 writable,SEIP 也可以由 PLIC set clear
- s 态中断没有被代理
如果中断被代理,根据信息 1 第 3 条,不能进 m-mode。根据信息 2,如果满足下列条件,trap 进 s-mode:
- 此时处理器为 s,需要 sstatus 的 SIE 为 1
- 根据信息 3,此时中断已经被代理,sip sie 中可以看到 mip mie 的 SEI STI SSI,只要相应的位为 1 就可以
-
处理器 m,中断 m
根据信息 1,如果满足下列条件,trap 进 m-mode:
- 此时处理器为 m,需要 mstatus 的 MIE 为 1
- mip mie 相应的位需要为 1,MEIP MTIP MSIP 都是 read-only,由 PLIC CLINT set clear
- m 态中断不能被代理
-
处理器 m,中断 s
如果中断没被代理,根据信息 1,如果满足下列条件,trap 进 m-mode:
- 此时处理器为 m,需要 mstatus 的 MIE 为 1
- mip mie 相应的位需要为 1,SEIP STIP SSIP 都是 writable,SEIP 也可以由 PLIC set clear
- s 态中断没有被代理
如果中断被代理,根据信息 1 第 3 条,不能进 m-mode。根据信息 2,不满足条件 1 (处理器特权级小于等于 s),所以也不能 trap 进 s-mode。
所以这种情况下,中断不被响应。
RISC-V 特权级文档 medeleg mideleg 部分有举例子。
-